|
|
Alchemist WebPick Awarded by the webzine of ChemWeb.com Leffingwell & Associates
|
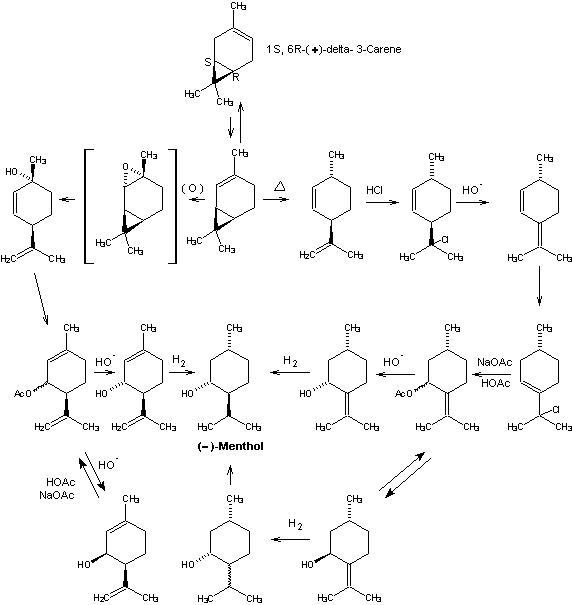
Beverage-Master 2011 - NEW - A new version with enhanced features for Excel 2007 & 2010. The world's leading program for beverage development. Juice-Master 2011 - NEW - A new version with enhanced features for Excel 2007 & 2010. The leading program for development of juice containing beverages. (+)-delta-3-Carenc from Western U.S. turpentine provides
another monoterpeiie raw material for the potential
production of (-)-menthol. Catalytic isomerization provides
the needed (+)-delta-2-carene required for either of two
alternate synthetic routes. In one approach, reaction of
(+)-2-carelie with peracid yields
(+)-cis-2,8-p-menthadien-l-ol via the intermediate
cis-2-carene epoxide. Allylic displacements with acetic or
formic acid in a buffered solution affords a mixture of cis-
and trans-piperitenyl acetates (or formates) which on
hydrolysis give (+)-cis- and (-)-trans-piperitenol. These
isomeric alcohols are separated by fractional distillation
and the cis-isomer is recycled by the same buffered
carboxylic acid system used above to mixed cis & trans
piperitenyl esters. In this manner pure
(-)-trans-piperitenol is obtained with minimum losses due to
(+)-cis isomer formation. The
A second route, developed by Hercules, Inc., involves pyrolysis of (+)-delta-2-carene to (+)trans-2,8-p-menthadiene with generation of an asymmetric center at C-1 which is carried through the remainder of the synthesis. Isomerization of this 2,8-menthadiene to (+)-2,4(8)-p-menthadiene can be accomplished either catalytically in the presence of strong bases (e.g., potassium t-butoxide) or via hydrochlorination-dehydrochlorination. Treatment of (+)-2,4(8)-p-menthadiene with hydrogen chloride affords 8-chloro-3-p-menthene which can be reacted with sodium acetate and acetic acid to give mixed (cis/trans) pulegol esters via allylic displacements. Hydrolysis affords (-)-cis and (+)-trans-pulegol. Because the absolute configuration of C-1 is fixed in this system, reduction of either pulegol isomer provides menthol isomers which can be readily equilibrated to predominently (-)-menthol. More specifically, reduction of (-)-cis-pulegol affords (-)-menthol and (+)-neoisomentliol, while (+)-trans-pulegol gives (+)-isomentliol and (+)-neomenthol. Purification of equilibrated menthol isomers is carried out by fractional distillation and crystallization of menthol derivatives. This latter process is intrinsically one of the most attractive potential routes to (-)-menthol developed to date but was never commercialized.
1. Leffingwell, J.C. & R.E. Shackelford, Laevo-Menthol - Syntheses and organoleptic properties, Cosmetics and Perfumery, 89(6), 69-89, 1974 2. Hopp, R., Menthol: its origins, chemistry, physiology and toxicological properties, Rec. Adv. Tobacco Science, Vol. 19, 3-46 (1993).
|
|
|
|
Copyright © Leffingwell & Associates
TERMS OF SERVICE.............PRIVACY POLICY