|
|
Alchemist WebPick Awarded by the webzine of ChemWeb.com Leffingwell & Associates
|
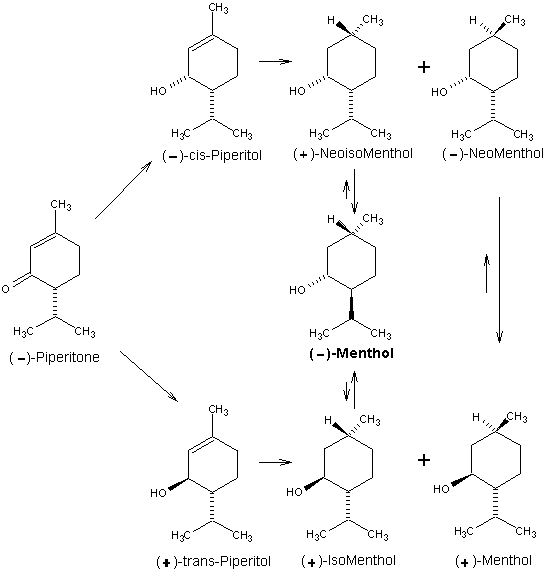
Beverage-Master 2011 - NEW - A new version with enhanced features for Excel 2007 & 2010. The world's leading program for beverage development. Juice-Master 2011 - NEW - A new version with enhanced features for Excel 2007 & 2010. The leading program for development of juice containing beverages. (-)-Piperitone is a major constituent of Australian oil of Eucalyptus dives. This material presents a somewhat different case because the optical activity is due solely to the asymmetric C-4 carbon which possesses the opposite configuration present in (-)-menthol. This means that to achieve the correct configuration we must selectively induce the correct asymmetry at C-1 and then invert C-4 in the final product. Because C-4 is adjacent to the ketone carbonyl, (-)piperitone is easily racemized in the presence of either acidic or basic substances. For this reason much effort has been expended to find a simple procedure for preparing optically pure piperitone from a partially racemized mixture. Hydrogenation of the 1,2-double bond of piperitone produces (+)-menthone and (+)-isomenthone. Since these ketones are of the opposite optical series with respect to C-1, on reduction with sodium in alcohol, (+)-menthone gives (+) -menthol while (+)-isomenthone gives (-)-menthol. This drawback precludes production of (-)menthol by this sequence due to partial racemization. Alternatively, (-)-piperitone may be reduced"' to a mixture of (+)-trans-piperitol and (-)-cis-piperitol (64% trans and 36% cis) using LiAIH4. Hydrogenation of (+)-trans-piperitol with Raney nickel produces (+)-isomenthol (major product) and (+)-menthol (minor product), while (-)cis-piperitol affords (-)-neomenthol (major product) and (+)-neoisomenthol (minor product). Isomerization of (+)-isomenthol and (+)-neoisomenthol in the presence of oxidation-reduction catalysts can produce (-)-menthol; (-)-neomenthol, however, isomerizes to (+)-menthol. As can be seen, this process is plagued with isomer separation of materials whose configurations at requisite asymmetric centers are antipodal. For this reason, (-)-menthol of high optical purity is rarely ever produced from (-)-piperitone without some optical resolution being required at a final purification stage. 1. Leffingwell, J.C. & R.E. Shackelford, Laevo-Menthol - Syntheses and organoleptic properties, Cosmetics and Perfumery, 89(6), 69-89, 1974 2. Hopp, R., Menthol: its origins, chemistry, physiology and toxicological properties, Rec. Adv. Tobacco Science, Vol. 19, 3-46 (1993).
|
|
|
|
Copyright © Leffingwell & Associates
TERMS OF SERVICE.............PRIVACY POLICY